THE ESSENTIAL GUIDE TO SAFETY GLASSES:PROTECTION MEETS PURPOSE
1. When are safety glasses required?
- Workplace hazards: OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) mandates the use of appropriate eye or face protection when employees are exposed to eye or face hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.
- Specific activities: Safety glasses are essential during tasks involving grinding, cutting, drilling, welding, brazing, working with chemicals or biological contaminants, or in dusty environments where airborne particles can be a risk.
- Home and DIY projects: Even seemingly simple tasks around the house, like lawn mowing, chopping wood, using strong cleaning products, or engaging in DIY projects, pose potential risks and warrant the use of safety glasses.
- Sports and recreation: Sports like racquetball, basketball, hockey, or outdoor activities like mountain biking, rock climbing, and fishing involve fast-moving objects or environmental hazards that can cause eye injuries, making safety glasses a necessary precaution.
- Classrooms and laboratories: Students conducting experiments in science labs should always wear safety glasses to protect their eyes from chemicals, glassware, and other hazardous materials.

2. Types of hazards requiring protection
- Impact: Flying debris, particles, chips, sand, and dust.
- Chemicals: Splashes, gases, vapors, acids, and caustic liquids.
- Heat: Hot sparks, molten metal, high-temperature exposure.
- Radiation: Welding, laser use, UV radiation.
3. Key features of OSHA-approved safety glasses
- Impact resistance: Must meet or exceed ANSI Z87.1 standards for impact resistance to protect against flying debris and particles.
- Side shields: Provide additional protection against lateral hazards.
- UV protection: Shield the eyes from harmful UV rays.
- Optical clarity: Lenses must provide clear vision without distortion.
- Durability and fit: Should be durable, comfortable, fit snugly, and be easily cleanable.
4. Selecting the right type of eyewear
- Safety glasses: Provide impact protection and are suitable for tasks with moderate impact risks, like woodworking or construction work.
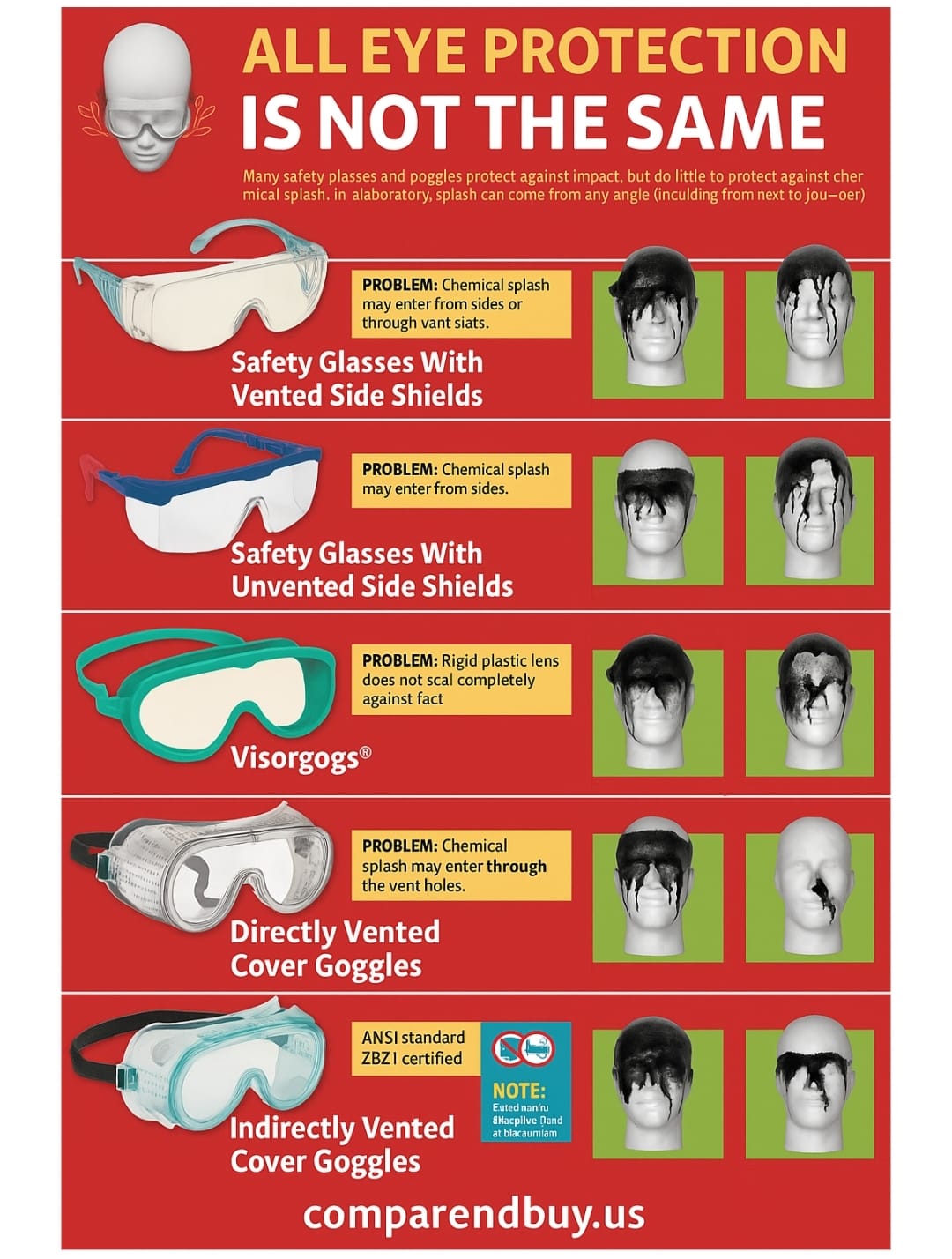
- Safety goggles: Offer greater protection with a seal around the eyes, ideal for working with chemicals, hazardous substances, or fine particles.
- Face shields/helmets: Provide broader protection, covering the entire face, but should be used in conjunction with safety glasses or goggles.
Remember, selecting the correct eye protection depends on the specific hazards in the workplace or environment. Always consult with safety experts or supervisors if unsure about the best eye protection for a particular task
Safety glasses have evolved far beyond basic eye shields. Today’s market offers a range that balances high-performance protection, comfort, style, and even environmental sustainability. Here’s what you need to know:
1. 👁️ Safety & Standards
- Every pair is typically ANSI Z87.1+ certified, ensuring they withstand high-speed impacts and molten metal spatter.
- Most lenses filter 99–100 % of harmful UVA, UVB, and UVC rays, essential for outdoor or intense UV exposure tasks (Protective Industrial Products, Global Industrial).
2. Lens Coatings & Types
3. Comfort & Fit
4. Sustainability
- The ECO Series™ from PIP merges safety with sustainability using bio-based and recycled materials, significantly reducing reliance on fossil-fuel-derived plastics (Protective Industrial Products).
- Frames and lenses are crafted from recycled PET bottles, bio-based polyethylene, and recycled polycarbonate while maintaining industry-standard durability (Protective Industrial Products).
5. Frame Styles & Applications
- Rimless and frameless models deliver minimal weight, compact storage, and relaxed style (Global Industrial).
- Full-frame, half-frame, and gasketed designs suit different environments—from construction and labs to manufacturing floors (Global Industrial, Global Industrial, Global Industrial).
- Some models (e.g. Jackson SG, Ergodyne Skullerz®) add venting, rubberized temple tips, and shade 5 IR options for welding support (Global Industrial).
🔍 Highlighted Safety Glass Picks
ECO Series™ Bio‑Based Full‑Frame
- Made from recycled materials (e.g., PET bottles) and bio-based PE fibers
- Features FogLess® 3Sixty™, anti-scratch coating, 8-base curvature, and ANSI certification (Protective Industrial Products)
Global Industrial Frameless Anti‑Fog
- Lightweight design ideal for storage and general industrial use
- Clear lens with anti-fog treatment, ANSI Z87.1 compliant (Global Industrial)
Jackson Safety SG Glasses
- Anti-scratch, anti-fog lenses with full UV protection
- Shade 5 IR option for welding, robust ANSI-approved frame (Global Industrial)
ERB Octane Wraparound
- 8.5 base curve with rubber temple tips for secure fit
- Scratch-resistant, anti-fog coating, comfortable wraparound style (Global Industrial)
3M Virtua™ with Foam Gasket
- Anti-fog lens combined with a foam gasket makes it perfect for humidity and wind-prone areas (Global Industrial)
✅ Choosing the Right Pair
|
Needs
|
Best Features
|
|
Impact & debris protection
|
ANSI Z87.1+, wraparound design, full-frame
|
|
Fog/chill resistance
|
Hydrophobic or anti-fog coatings, foam gasket
|
|
Long-term comfort
|
Ergonomic nose pads, flexible temples
|
|
UV or high-glare work
|
Gray/amber lenses, 99%+ UV filters
|
|
Eco-conscious procurement
|
Bio-based, recycled materials (ECO Series™)
|
REGULATIONS & STANDARDS FOR SAFETY GLASSES
🛡️ 1. Key Standards & Regulatory Bodies
- **ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 (USA)**
– Defines basic (Z87) and high-impact (Z87+) protection.
– Requires rigorous tests like the drop ball (basic) and high‑velocity projectile (high-impact) (Wikipedia).
- OSHA (USA)
– Enforces workplace eye safety; mandates compliance with ANSI Z87.1 (State Farm).
- MIL-PRF-31013 (US Military)
– Sets ballistic eyewear standards: withstands 0.15 caliber rounds at ~200 m/s (Wikipedia).
- **EN 166 / EN Standards (Europe)**
– EN 166 covers general eye protection.
– Impact levels: F (low), B (medium), A (high), along with splash/dust codes (Wikipedia, SafetyGearPro.com).
- ISO 12312 (Sunglasses)
– For UV protection; falls outside industrial safety purview (Wikipedia, Wikipedia).
⚙️ 2. Testing & Markings
|
Standard/System
|
Test Type
|
Markings
|
|
ANSI Z87.1
|
Drop ball + ¼″ steel bullet @150 ft/s
|
Z87 (basic) / Z87+ (high-impact)
|
|
EN 166
|
Steel shots, dust, splash resistance
|
F, B, A, + codes (UV, splash)
|
|
MIL-PRF-31013
|
0.15 cal projectile test
|
Military-specific markings
|
🔍 3. Lens Markings & Filters
- **ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 lens codes**:
– Impact: Z87+
– UV protection: U with a number
– Infrared: R with a number
– Welding filters: W shade number (Wikipedia, SafetyGearPro.com)
- **EN 166 Lens Markings**:
– Droplet/Dust: D
– UV: U
– Optical clarity: 1, 2, 3, etc.
🏭 4. Use-Case Guidance
- Industrial/Construction: ANSI Z87+ or equivalent EN high-impact protection.
- Military/Ballistic: MIL-PRF-31013 + ANSI Z87+; must pass high-speed projectile tests (Wikipedia, Wikipedia).
- Chemical Labs: EN-rated splash/droplet resistance + anti-fog sealing.
- Welding & Lasers: Specific shade numbers and laser-specific goggles per ANSI Z136 and EN 207 (SafetyGearPro.com, Wikipedia).
✅ 5. Tips for Compliance & Safety
- Always check markings: Z87+, EN 166 F/B/A, MIL-PRF, filter codes.
- Ensure side shields or goggles to block lateral hazards.
- Choose correct lens tint and filter for UV, IR, laser, or welding work.
- Replace eyewear if damaged—safety-tested lenses must stay intact.
- For prescription needs, opt for certified 😀 ANSI Z87+ Rx eyewear.
🔧 Bottom Line
Safety glasses aren’t one-size-fits-all. Regulatory standards ensure protection—but only if the eyewear matches your hazard. Look for the right markings, test ratings, and coatings, and you’ll keep your vision safe in any environment.
Safety glasses aren’t just a compliance item—they're a critical safeguard that empowers workers to perform comfortably and confidently. Whether you're navigating sustainability goals with eco‑friendly eyewear or optimizing visibility and fit, today’s options cover all bases. Make sure your selected pair meets ANSI standards and fits your specific work environment—your vision depends on it. 👀
Eye Injury Incidents from Not Wearing Safety Glasses : Shocking Trends and Why Protection Matters
Every day, over 2,000 eye injuries occur in the workplace—a staggering number, and a significant portion of these incidents could have been prevented with one simple measure: wearing safety glasses.
Eye Injuries in the Workplace: The Stark Reality
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA):
- Over 700,000 eye injuries happen on the job annually in the U.S.
- Approximately 90% of these injuries are preventable with proper eye protection.
- Construction, manufacturing, and lab work are among the top industries with the highest rates of incidents.
What Happens When Safety Glasses Aren’t Worn ?
Failing to wear protective eyewear can lead to:
- Corneal abrasions from flying particles
- Chemical burns from splashes and fumes
- Radiation exposure from welding arcs or lasers
- Puncture injuries from tools or machinery
- Long-term vision loss or even blindness
Cost of Eye Injuries to Businesses and Workers
- Direct medical expenses: $300M+ annually
- Lost productivity: Thousands of workdays missed
- Workers' compensation claims: High severity ratings due to long recovery periods
- Legal liability for non-compliance with ANSI Z87.1 and OSHA standards
Common Causes of Eye Injuries
|
Cause
|
% of Cases
|
Example Scenarios
|
|
Flying or falling objects
|
70%
|
Grinding, hammering, chiseling
|
|
Contact with harmful chemicals
|
20%
|
Cleaning agents, acids, solvents
|
|
Exposure to harmful radiation
|
7%
|
Welding, UV light, lasers
|
|
Inadequate eye protection
|
~60%
|
No glasses, improper type or fit
|
Real-Life Case Example
In a 2023 incident at a manufacturing plant, an employee suffered partial vision loss due to molten metal splashing into his eye. Investigation revealed the worker had removed his safety glasses temporarily due to fogging. This led to a six-figure workers' comp claim and a full OSHA investigation.
Top Reasons Workers Skip Safety Glasses
- Discomfort or poor fit
- Fogging or distortion
- Lack of awareness or training
- “It won’t happen to me” mindset
Preventing Eye Injuries: Best Practices
- Mandatory PPE policies in all eye-risk zones
- Provide ANSI Z87.1-compliant safety glasses
- Anti-fog, anti-scratch coatings to reduce complaints
- Regular safety training and compliance checks
- Eye wash stations near hazardous areas
Choose the Right Safety Glasses for Your Industry
At CompareAndBuy.us, we help businesses find the best safety glasses tailored to their specific industry needs—whether it's impact-resistant lenses, chemical splash goggles, or welding shields.
🔎 Compare brands, features, standards, and prices across top vendors like Global Industrial, Uline, PIP Global, and more—all in one place.
Final Word
Wearing safety glasses isn't optional—it's essential. The data is clear: eye injuries are common, costly, and largely preventable. Don’t become a statistic. Protect your team, productivity, and peace of mind with the right safety gear.

